Common Stock: What It Is, Different Types, vs Preferred Stock

Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. Tickmark, Inc. and its affiliates do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice. The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal, tax or accounting advice or recommendations. All information prepared on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be relied on for legal, tax or accounting advice.
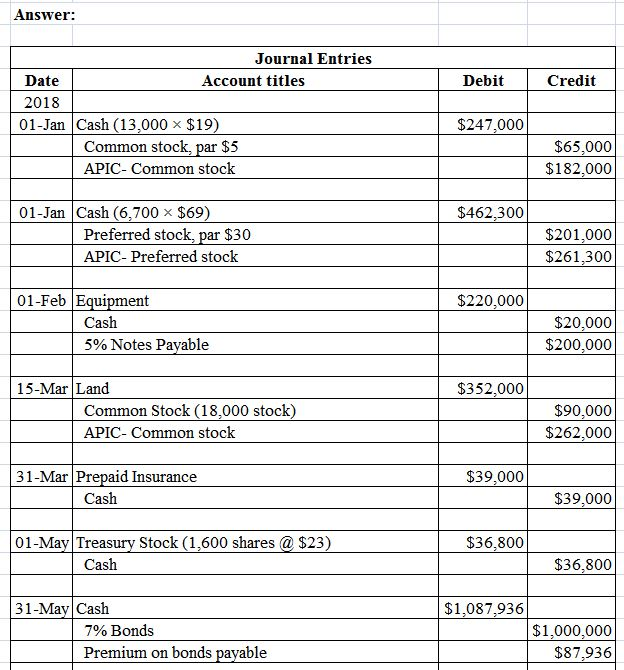
Accounting for common stock issues
Issued Shares are the number of shares that company sells to investors. They are the authorized shares that sold to the investors in the market. They will receive cash as the number of shares are sold to the investor. Moreover, the company may issue a share to acquire another company by giving the business owner share equity. The common stock that company buyback from the market is recorded as treasury stock in the balance sheet. It is the negative balance report in the equity section in the balance sheet.
Price stability
- With the right balance, common stocks could help you reach your financial goals over time.
- Adjustment entries are an important part of the accounting period and the accounting cycle.
- The first step to buying common stocks is to open a brokerage account.
- The debit impact of the transaction is the receipt of the cash against the issue of the preferred shares.
- Thus, par value is said to represent the “legal capital” of the firm.
The stock market offers a wide range of companies across various sectors and industries. If you invest in a diverse set of common stocks, you can spread your risk and reduce the impact of a poor-performing stock on your overall portfolio. Diversification is a fundamental principle of sound investing, and common stocks provide an effective way to achieve it.
Common And Preferred Stock
Stockholders’ equity is the difference (or residual) of assets minus liabilities. When its articles of incorporation are prepared, a business will often request authorization to issue a larger number of shares than what is immediately needed. However, because of how they differ from common stock, investors need a different approach when investing in them. The first-ever common stock was issued in 1602 by the Dutch East India Company and traded on the Amsterdam Stock Exchange.
Deferrals are revenues or expenses that have been paid or received in advance. To record a deferral, an accountant would debit an asset account and credit a revenue or expense account. Adjustment entries are an important part of the accounting period and the accounting cycle.
Each slice represents a share owned by investors, called common stockholders. Owning a slice means owning a part of the company, including rights to vote and earn dividends. Adjustment entries are made at the end of an accounting period, which can impact the timing of when revenue and expenses are recorded. For example, if an adjustment entry is made to defer revenue to a future accounting period, this will delay the recognition of revenue until the future period.
Hence, the following options can be a good idea to further explore. The prices of the share price fluctuate depending on the demand for shares. For instance, if the market is optimistic about specific shares, its demand increases and leads to an increase in price.
Selling preferred stock, like any other shares, lets a company raise money by selling a stake in the business. A company may do this to raise capital for business expansion, debt repayment, or to invest in new projects. Preferred stocks are less dilutive of company ownership since they do not come with voting rights. They offer the issuing firm other benefits, not least because being less volatile makes them appeal to different investors.
The company simply increase the number of outstanding share by a specific time and keep the total dollar value of share the same. Price per share will decrease align with the number of share spotify for public or commercial use increases. The company needs to reverse the treasury stock with common stock and additional paid-in capital. The company can retire stock by buyback the outstanding stock from the market.
Assume a corporation has been authorized by the state in which it is organized to issue 500,000 shares of common stock with no par value. If the corporation actually issues only 100,000 shares for $50 each, the corporation will debit its Cash account for $5,000,000 and will credit its account Common Stock for $5,000,000. The corporation will now have 100,000 shares of common stock outstanding. If a stockholder owns 1,000 shares of the common stock, the stockholder owns 1% of the corporation. If the corporation declares a divided of $0.10 per share, this stockholder will receive a dividend of $100 (1,000 shares X $0.10).

